The UK needs new low-carbon electricity generation to meet our commitment to reduce net greenhouse gas emissions to zero by 2050.
As an interim target, the Labour government is aiming to decarbonise electricity generation by 2030. As transport and heating also need to be decarbonised by moving from fossil fuels to electric power, total electricity demand is expected to double by 2050 – which means that the UK will potentially need to quadruple its low-carbon generation in less than three decades.
An array of independent analysis and modelling studies have concluded that net zero needs nuclear to provide reliable baseload power which can balance the variability of wind and other renewables, and reduce the total costs of decarbonising the energy mix.
This page was last updated in September 2024.
Current fleet
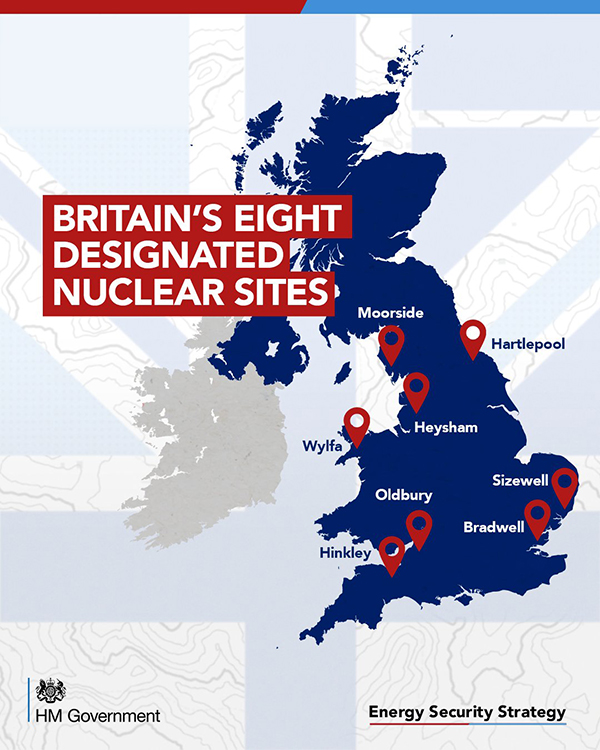
The UK currently has five operational nuclear power plants, owned by EDF, with a total capacity of 5.9GWe. All are now reaching the end of their operational lives.
In recent years, the UK nuclear fleet has generated around a fifth of the UK’s electricity – around 65 terawatt-hours (TWh) a year – from eight reactors. Seven of these are advanced gas-cooled reactors (AGRs) built over the 1960s–80s, all of which are scheduled to retire this decade.
Three AGRs – Dungeness B, Hunterston B and Hinkley Point B – have already ceased generation. Hartlepool and Heysham 1 are scheduled to cease production by 2026, and Heysham 2 and Torness in 2028. Decommissioning of the AGR fleet will be managed by Nuclear Restoration Services (formerly Magnox).
The other operational nuclear power station is Sizewell B, the UK’s only pressurised water reactor (PWR), with a generating capacity of 1.2GWe. Sizewell B began operations in 1995, and was scheduled to retire in 2035. EDF has announced plans to extend its life by at least 20 years, allowing it to contribute to the 2050 target.
For the latest information, see EDF’s page on its UK nuclear power stations.
New reactors & GDA
Four gigawatt-scale reactor designs have been formally approved for new build in the UK:
- Framatome’s EPR (originally the Areva European Pressurised Reactor) is a generation III+ PWR, offering a range of safety, economic and operational improvements over previous designs, and an output of 1.6GWe. Two EPRs are now under construction at Hinkley Point C in Somerset. EPRs are also under development or operational in Finland, France and China.
- Westinghouse’s AP1000 is also a Gen III+ PWR, with an output of 1.1GWe. AP1000s are under construction or operational in China and the US.
- The 1.3GWe Hitachi-GE Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR) operates at lower pressures and temperatures than PWRs, and features a much larger pressure vessel. Four ABWRs are in operation in Japan.
- The Chinese Hualong HPR1000 is a 1.17GWe PWR. Three reactors are operational in China and two in Pakistan, with another 11 under construction in China.
These four reactors have all completed the UK’s generic design assessment (GDA) by the Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) and Environment Agency. This assessment is intended to support the construction of a number of new nuclear power stations by approving a standard reactor design which can be built in different locations by different developers. Each build will still require a site-specific licence.
The UK is also considering the development of small modular reactors based on Gen III+ technologies, as well as new designs of advanced modular reactors based on Gen IV technologies.
The Rolls-Royce SMR, a 470MWe PWR, formally entered GDA in early 2022. Other SMRs to begin the process include Holtec’s SMR-300 and GE Hitachi’s BWRX-300, both with funding support from the government’s Future Nuclear Enabling Fund. Westinghouse’s AP300 has also been approved to start GDA.
See the ONR’s GDA pages for the latest information.

 In 2024, the UK government held a
In 2024, the UK government held a 

